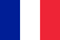
So far, science is known for 280 species of worms that can develop and live in the human body, parasitizing in various organs and tissues.The frequency of human infection depends on the climate and socio-economic conditions of specific territories (in underdeveloped countries, especially those located in the tropical and subtropical zone, the level of parasitic infections is much higher than in economically developed countries).
Helminths human infection methods:
- Biogelmintosis (animal infection).
- Helminthoses contagioine (transmitted from person to person).
- Geogelmintoses (diseases caused by parasites who perform one of the life cycles on Earth).
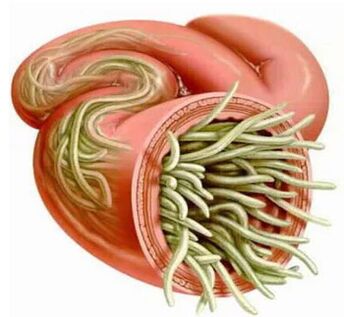
Factors that influence the manifestations of helminthiasses
The method of penetrating the parasite into the body:
- The degree of adaptation of helminth in the human body;
- Population density (quantity) of parasitic individuals;
- The worm habitat (tissue parasites live in the thickness of the soft tissue, and the cleaning lives in the hollow gaps).Some helminths at different stages have an educational and fabric forms.The stages of larvae and the development of worms, as a rule, cause more pronounced pathological changes.
In the absence of new infection, the number of adult parasites in the human body does not increase.This feature significantly distinguishes helminthic invasions from diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and simple organisms.
Worms in humans: Symptoms
Helminthosis is a disease characterized by 2 phases of the course (acute, from two weeks to two months) and chronic (from several months to several years).
Symptoms of acute phase of helminthiasis
The first signs of the disease can manifest at different times (most often after 2-3 weeks, with ascaridosis-after 2-3 days, and with phyiriosis, the incubation period can last 6-18 months).
In the acute phase of parasitic occupation, the most characteristic symptom is an allergic reaction (antibodies are generated against antigens of parasitic migratory larvae).Often, itching rashes, prone to repeated course, have an increase in repeated course, regional lymph nodes appear on the skin, and the appearance of generalized or local edema, muscle and articular pain may occur.Also, parasite migratory larvae can cause chest pain, coughing, drowning drowning, excrement disorders, nausea and vomiting.
At the same time, the acute phase of helminthiasis can be associated with more serious disorders (severe forms of pneumonia, hepatitis, allergic myocarditis, hepatosterogalia (an increase in the liver and spleen).
In the blood, the amount of eosinophils (eosinophilia) increases and the normal quantitative ratio between protein fractions (dysproteinemia) is disturbed.
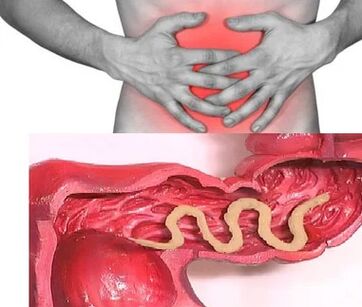
Signs of chronic helminthiasis
The symptoms of the chronic phase depend directly on which organ is "populated" with parasites, as well as their size and quantity play an important role.
So, when the parasite in the intestines of single individuals, the disease can occur asymptomatic (except in cases of infection with very large parasites).The characteristic characteristics of the chronic phase of intestinal helminthiasis are dyspeptic disorders.In children, acenoarotic syndrome and pain is more pronounced.With massive occupation ascarids, intestinal obstruction, mechanical jaundice and pancreatitis is possible.
By consuming all the substances needed for their vital activity by the host body, poisons cause digestive disorders, violations of the absorption of vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, proteins and fats.At the same time, worm's life products inhibit normal intestinal microflora and reduce the body's immune forces.
In people suffering from Helminthias, due to the weakened immunity and the enhanced cell division process (the consequences of continuous restoration of tissue parasites), the risk of malignant tumors increases significantly.
Types of parasitic helminths in the human body
The causative agents of human helminthiasis are 2 types of worms: round (nematoda) and flat (strips and plates).
Round worms
Pinworm
The parasites that are the cause of enterobiosis are thin (up to 10 mm) cavity worms that have white gray stain.The infection occurs in a nutritious way (through the mouth).The reason for this is dirty hands.Parasite eggs can be on the ground, on the wool of infected animals, vegetables and unwashed fruits, etc.At the same time, with enterobiosis, cases of self -wishes (especially children) that occur as a result of combing areas and subsequent swallows of eggs are not uncommon.The cutting larvae takes place within two weeks in the digestive tract.Turning to an adult individual, the worm parasitizes in the lower parts of the small and upper parts of the colon.
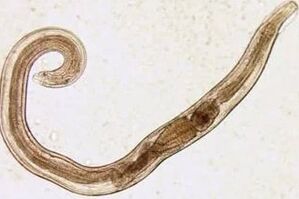
Ascarida
Askaride is a large parasite of a yellow-red finger shape, reaching an adult state of 40 cm (female) and 15-25 cm (male).Without a suction cup or other fixed equipment, ascaride can move independently to food measures.Eggs determined by the female parasite are distinguished by feces.
Acadeosis infection occurs in case of ingestion of ripe eggs along with water or vegetables and unwashed fruits on which there are particles of soil.Once the eggs penetrate the gut, the ripe larvae come out of them.Then, by inserting into the wall of the intestine, they reach the heart according to the bloodstream, and from there they fall into the lungs.Through the pulmonary alveoli, the larvae and the ascarida through the respiratory tract penetrate the oral cavity.After repeated swallowing, the parasite reaches the small intestine, where it develops in an adult.The worm lives for 12 months, then dies and stays with feces.In the intestines of an owner can live one or several hundred individuals.
Vlashev
Vlasov, the causative agent of trichocephalosis, is a white helminth that parasitizes in the initial part of the large intestine and reaches a size 4-5 cm.The parasite is fed by blood and rectal mucosa tissues.
The female -paved eggs on the intestinal walls emerge along with the feces.Their development occurs in the environment (optimally on Earth).Eggs with parasite larvae penetrate the body in a nutritious way, through dirty hands, with water or vegetables and unwashed fruits.
Trichinella
The causative agent of trichinellosis is a small round helminth that reaches 2-5 mm in length.The infection occurs when the use of poorly fried meat (pork, bear cub, wild boar).By penetrating the intestine, the parasite larva in 3-4 days matures in the condition of the sexually mature individual.The lifespan of the worm is 40 days, after which the parasite dies.By running the intestinal wall, the larvae penetrate the bloodstream and are carried into all organs of the human body, being placed in the muscles.In this case, the respiratory and facial muscles, as well as the muscles-ado-outs of the limbs, are most often affected.
In the first days after the invasion, patients complain of abdominal pain.Then, after about 2 weeks, the body temperature rises to 39-40 s, itchy rashes appear on the skin, muscle pain develops and the face swells.In this period, in the case of mass infection, there is a significant risk of death.After about a month, recovery occurs.The parasite is caught in a spiral form, after which it dies within two years.
Ankylostoma and not -kore
These two parasites are similar to each other from biological characteristics as well as in the diseases caused.With this, it is customary to attach them under the general name (ankylostoma).Worms reaching 10-15 mm length are parasitized at 12-P.It should be noted that this is one of the most common, but at the same time, rarely identified parasites.Worm worms penetrate the human body through the skin when in contact with the infected soil.Further, by getting into the bloodstream, they, like ascarides, migrate to the lungs, and then, through the bronchitis, along with the cast saliva - in the digestive tract.Anquilostoma parasitizes in the intestine, attaching the intestinal wall.A parasite that eats exclusively with blood bites the blood vessels by drilling the mucous membrane, injecting an anti -damaged ingredient there.During the day, an adult can absorb on average 0.05-0.35 ml of blood.Therefore, the most characteristic symptom of this helminthiasis is the anemia of iron deficiency, as well as a change in the ratio of protein fractions (disproteinemia).
Flat worms
Tape
This is one of the largest helminates that reaches a length of 10-20 meters.The disease caused by this parasite is called dipillobotriosis.The worm development cycle begins with freshwater fish or crustaceans.The larva enters the human body, which is the last owner of a wide ribbon with infected or infected fish fillets.The reach of the small intestine, the parasite is glued to its wall and for 20-25 days grows in a sexually mature individual.
Hepatic bacon
A parasite that causes opisthorchiasis is a flat worm that reaches a length of 7-20 mm.It should be noted that more than 50% of cases of infection with a liver pan (also called a cat biconomate) falls on Russian residents.The parasite larvae begin to develop as the eggs fall into fresh water (from swallowed snails).Then they penetrate the body of the fish (carp, crap, bream, roach).Human infection occurs when you eat infected fish meat that has not suffered sufficient heat treatment.The hepatic bomb larvae from the small intestine penetrates the bile ducts and the gall bladder, fixing there with two suction cups.
damage
These almost identical parasites in the structure reach a length of 5-6 meters.Infection with tusarinhosis and tusiasis occurs due to the use of livestock or pork infected with Finnish (one of the intermediate forms of helminthiasis).The visible Finns, presented in the form of white bubbles, reaching 0.5 cm in size, are glued to the wall of a person's small intestines and are transformed into an adult individual in 3 months.The ribbon parasite, consisting of more than 2000 segments, is steadily increasing.At the same time, the bottom segments containing eggs are descended and moved independently along the colon at the anal opening, and then crawl from the anal, or come to the outer environment along with the feces.The most characteristic symptoms of helminthiasis are a violation of the digestive tract.
echo
For this parasite, a person is an intermediate host.The worm parasitizes in the human body in the form of Finns.The last owner of Echinococcus is a wolf, dog or a cat.The infection occurs in an alimentary manner in contact with animals and environmental objects, with a small portion of echinococcus eggs.Once you have entered the intestines, the oncospheres (sixth black larvae) develop from them.From the gut they penetrate the bloodstream and carry throughout the body.
Alveococcal
This parasite, which is considered a variety of echinococcus, is the cause of one of the most dangerous helminthias (alveococcosis), which is similar in severity with cirrhosis and liver cancer.The infection occurs with the penetration of the oncosphere (eggs with mature larvae) into the intestines.There, the embryo comes out of the egg and, inserting into the intestinal wall, penetrates the bloodstream.Further, with a blood flow, the parasite spreads through all the tissues and organs of the body (most often localized in the liver).It is there that the main stage of development begins in the larvae (a bubble of very taste, laurelocyst) is formed).The room contains an embryo head of a parasite, which continues to develop gradually.Lavrocists are very aggressive formations that grow constantly due to the growth of bubbles, as well as have the ability to grow in the liver, such as cancer metastases.
Diagnosis of helminthiasis
The diagnosis of helminthic invasions includes the following events:
- A complete collection of an anamnesis that helps to detect possible causes of infection;
- Laboratory studies for feces, blood, intestinal contents 12p, rectal and perianal mucosa, muscle tissue, pulmonary saliva, bile.During the analysis, eggs, segments or fragments of parasites can be detected.At the same time, the increased content of eosinophils in the blood is also a signal about the presence of helminthiasis.
- In the diagnosis of diseases caused by larvae stages or tissue parasites, serological studies have been conducted (ELISU, RSC, indirect agglutination, immunofluorescence analysis, etc.) performed.
- To identify poisons that affect liver tissue, ultrasound, CT and endoscopic studies are prescribed.
Worms in humans: Treatment
In the acute phase of a parasitic infection, the patient is prescribed detoxification and desensitizing therapy.In a severe course of the disease (trematodosis of the liver, trichinellosis), glucocorticoids are used according to medical indications.
As specific therapy drugs, taking into account the nature of the pathogen, special agents of chemotherapeutic anthelmintics are prescribed.
In parallel, the patient is recommended to take antihistamines and enterosorbents.The final stage of treatment involves the use of probiotics that normalize the intestinal microflora.
A special savings diet is also prescribed (the food should be easily soluble and contain a little fat).
During the period of anthelmintic therapy, the patient needs strict adherence to personal hygiene (in order to avoid re -infection).At the same time, with many helminthiasis, all family members and persons who are infected in constant contact must undergo treatment.